小编为大家整理了英国的银行体系中英对照,希望对你有帮助哦!
The Banking System in the United Kingdom英国的银行体系In the United Kingdom, financial institutions are categorized into two ma]or groups: the Recognized Banks and the Licensed Deposit Institutions. The criteria for each category are determined by the Bank of England~——the Central Bank. The Bank of England will consider the size of the institution, its management and also the number of participants who effectively direct the business, before decisions are made on the status of the financial institutions who apply for bank licenses in the United Kingdom.
Let us look at the Recognized Banks.
These banks provide a wide range of highly specialized banking services. According to the Banking Act 1979. "Recognized Banks" must satisfy the Bank of England of their high reputation and of their integrity, management and financial prudence. The wide range of services include: i. the acceptance of sight and time deposits); ii. loan and overdraft facilities; iii. foreign currency exchange and documentary credits and collections~; iv. financial advice for corporations and individuals; v. investment management and arrangements for the purchase and sale of securities.
As for Licensed Deposits institutions, they only provide a limited range of services. The prime services are still based on the acceptance of deposits from the public although they are not required to satisfy the rules laid down for Recognized Banks. To obtain a license, the institution must satisfy the Bank of England's requirement that all directors, controllers or managers of the institution must be an appropriate and proper person to hold that position and to conduce banking business in a proper manner.
Let us now look at the major types of financial intermediaries~ in the United Kingdom.
To begin with, we shall examine the role of the Clearing Banks. These are the dominating financial intermediaries in retail banking business~ in the United Kingdom. They handle the clearing functions of banks, and are responsible for most of the country' s cash distribution and money transfer functions, which include cheque payment services and also electronic fund transfers, etc.; The retail branch network of these banks is extensive with over 10,000 branches all over the country.
Another type of financial intermediaries in the United Kingdom are discount houses. Discount houses provide a primary channel through which the Bank of England operates in the discount market to implement its monetary policy. Because of their easy access to the money market, discount houses act as market-maker in bills since they are the major underwriters of the weekly issuers of the Treasury bills of the Bank of England. Therefore, discount houses not only provide short-term funds for the government, they provide a channel for banks to adjust their portfolio holdings, i.e., their liquidity positions.
The third type of financial intermediaries in the UK are the merchant banks~ and acceptance houses. Originally developed to handle businesses connection with trade, these merchant banks later expanded into foreign trade, foreign exchange and also bullion dealers. Many of the merchant banks are also acceptance houses. Indeed, their functions have now expanded considerably into major overseas operations, specializing in company financial advice, takeovers and mergers, underwritings which include the provision of additional capital through share floatation.
Finally, we should look at foreign banks in England. As a major international financial centre, London has acted as a magnet to over 450 foreign banks, which have set up representative offices, branches, or subsidiary companies. Business focus on these foreign banks cover foreign currency dealings, international finance deals to foreign companies and governments, trade finance services to business.
Notes
1.The Recognized Banks 认可银行,在英国特指可以全面经营银行业务的银行。认可银行要受到很严格的要求,凡达不到认可标准的机构均不得使用银行名称或字样,包括不得使用“投资银行”等字样。
2.The Licensed Deposit Banks 持牌存款银行,在英国特指一些业务范围受到一定限制,规模较小的银行机构。
3.The Bank of England 英格兰银行,英国的中央银行,创立于1694年,公认为全世界中央银行的鼻祖。
4.Sight and time deposits 活期和定期存款(参见Section 3)。
5.overdraft 透支,指银行客户在一定条件下和一定范围内可以超过自己帐户存款的余额用款,实为银行对客户的一种信贷便利。
6.collections 托收,指债权人委托银行向债务人收款的一种结算方式(参见Section 6)。
7.financial intermediaries 金融中介(机构),指作为放款者与借款者中间人的金融机构。金融中介的作用在于促进信贷活动,有利于评估借款者的信誉,以减少放款风险,降低资金成本。金融中介可分为存款性和非存款性两类。
8.the Clearing Banks 清算银行,在英国是零售银行的主要组成部分,包括伦敦清算银行、苏格兰清算银行和北爱尔兰银行。清算,是指银行间为结清债权债务关系而进行的一系列活动。
9.retail banking business 零售银行业务(与批发银行业务相对应),主要指对单独的客户的业务,如存款、放款、结算等。
10.discount houses 贴现商号,是英国金融制度中的独特事物。贴现行在英格兰银行与清算银行之间处于中心地位,主要通过贴现与再贴现传导英格兰的货币政策及英格兰银行对银行的管制。
11.discount market 贴现市场,在英国由贴现行作为市场主体,是英格兰银行实施货币政策的主要场所之一。
12.Discount houses provide a primary channel through which the Bank of England operates in the discount market to implement its monetary policy 贴现行为英格兰银行提供了一个在贴现市场上进行操作,实施货币政策的渠道。
13.market—maker 市场制造者,指一家金融机构或一个经纪人就一种货币或证券进行又买又卖的交易活动,保证其它交易者时刻都能找到交易对手。l羞南8
14.Merchant banks 商人银行,指经营部分银行业务的金融机构,主要办理承兑和经营一般业务,对国夕L的工程项目提供长期信贷和发放国外贷款。在60年代以后,还办理外汇交易,为客户保管证券,替一些基金会从事投资等。商人银行大部分存在于伦敦及一些英联邦国家。
15.cceptance houses 票据承兑银行,指专门从事承兑汇票业务或在其他人的票据上背 书业务的一种金融机构。
16.underwriting (证券)承销,指承销商从发行公司或政府实体买下新发行的债券,再 把这些债券直接或通过交易商售给公众,即实际承担了发行风险。这一过程中,承销商赚的 支付给发行者的价格和公众发售价格之间的价差,即承销价差。
参考资料
英国的银行体系
英国是世界上金融业最发达的国家之一。伦敦是英国的金融中心,也是世界上主要的国 际金融中心之一。伦敦的金融地位形成于英镑作为主要的国际储备货币的年代,而在二战后 随着英国经济地位的下降受到了削弱,但从本世纪七十年代以来随着美元危机和欧洲货币市 场的兴起,伦敦的金融中心地位又重新得到了恢复。
伦敦的优势在于具有相对稳定的.金融体系和政治环境,对国际银行业控制的相对自由,大批拥有丰富的专业知识和技能的银行家及不同层次的各种专业人材,优良的基础设施和通讯网络,在语言、时区及地理位置上的优越性等等。
除上述优势外,英国的银行体系也具有其自身的特点,下面我们分别加以介绍。
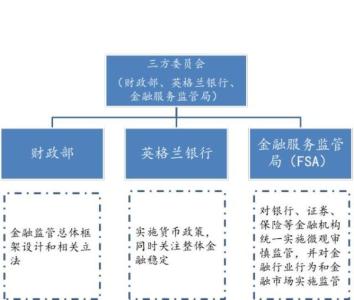
一、中央银行——英格兰银行
英格兰银行是英国的中央银行。1694年根据国王特准法成立,它是英国第一家注册的有限公司性质的股份银行。此时的英格兰银行并不是专门的中央银行,它同其它的私人银行一样,也办理一般的存放款业务。直到1833年,英国国会规定只有英格兰银行发行的钞票才具有无限法偿,从而奠定了英格兰银行作为英国中央银行的基础。1946年2月,英国政府颁布新的《英格兰银行法》,将英格兰银行的全部股本收归国有,从此,英格兰银行成为国有化的中央银行。
英格兰银行受政府财政部控制,为政府机构。英格兰银行在发表自身的观点上有一定的 独立性,是金融界中具有权威的代言人。英格兰银行除了依照银行法执行对银行业的监管之 外,还承担·了对金融市场的管理职能。英格兰银行在鼓励行业自律,尤其是在保险和证券业务中发挥了重要的作用。此外,英格兰银行还承担了管理英国的债务和外汇储备职能、管理和发行纸币及铸币的职能及政府的银行的职能,同时对政府的经济和货币政策提供顾问。
80年代以来调整后的英格兰银行的管理机构分为三大部分:(1)金融结构和监管,有银行监督处、金融结构和制度处。(2)政策和市场,有工业金融处、统计处、经济处、金边债券处、货币市场处、外汇处、地区处和国际处。(3)经营和服务,有营业部、注册处、印刷厂和工商服务部。
二、英国的银行机构
英国的所有的银行机构必须有英格兰银行的批准才可以吸收存款,一些特定的活动需要特殊的业务执照,但对不同的机构的活动没有很明确的限制。英国的银行机构主要可分为以下几种:
1.零售银行(Retail Banks)。在英国,清算银行是零售银行业务和货币传送活动的主要机构。这些银行属于英国最大的银行之列,同时也是英国最主要的国际性银行。
英国的清算银行主要分布于英格兰和威尔士,这些银行主要包括巴克莱银行(Barclays Bank)、国民西敏寺银行(National Westminster Bank)、米德兰银行(Midland Bank)、劳埃德银行(Lloyds Bank)、苏格兰皇家银行集团(Royal Bank of Scotland Group)、TSB集团等。另外,Girobank是由邮政局建立的提供一般性活期存款及货币运送服务的银行,也属于零售银行。
2.承兑行(Accepting Houses)。这些机构是属于承兑业协会的具有悠久历史的商人银行。其传统的业务是进行贸易融资,提供较大比例的承兑工具。现阶段虽然受到了银行业的激烈竞争,但其发行的票据仍可以在英格兰银行进行贴现。现在承兑行的业务已经扩大到企业融资、投资管理、贷款及银团业务领域。
3.商人银行(Merchant Banks)。商人银行的业务起源于十八世纪的欧洲商业活动。最初的业务是为商人的票据进行承兑,而后逐渐从原来的贸易融资服务发展到为政府和企业提供长期的资金以及其它专业性的服务和咨询。在英国,从事这类业务的金融机构称为商人银行,它具有向企业和政府提供专业性的服务和咨询的职能,而很少运用自身资本,类似于美国的投资银行。但是英国的商人银行具有一定的吸收存款的职能,可以归类为存款机构。
商人银行业务的发展与贸易和资本市场的发展有苞密切的联系。商人银行的业务大体包括短期和中期资金融通、长期融资、投资管理、经纪服务及其它新兴服务。与传统的商业银行相比,商人银行对市场的依赖性更强。
商人银行发展至今,主要有以下几种存在形式:一是商业银行通过兼并、购买、参股或建立附属公司拥有商人银行,这类方式现在较为普遍;二是独立的商人银行;三是全能性银行直接经营商人银行业务。
4.贴现行(Discount Houses)。贴现行构成了伦敦贴现市场协会。它由一些指定的银行的货币交易部门组成,从事高度专业化的银行业务,其主要业务包括:承销英格兰银行每周财政部票据的出售;进行英镑短期金融工具的交易,如政府票据、银行票据、商业票据、英镑存款证以及短期政府债券等;向英格兰银行进行追索(因英格兰银行为弥补短期资金的不足可以从贴现行购买票据或进行直接贷款)。
5.外国银行。从上一世纪开始,大量的欧美国家银行便在伦敦金融城里建立了自己的业务机构,使伦敦成为了国际性的金融中心。目前,在伦敦的外国银行大约有540家,包括外国银行和国际性合作银行的分行及其附属机构。
6.其他金融机构。其他金融机构包括建筑业协会(接收存款、为住房建设和购买提供融资)、融资公司(提供消费信贷)以及国民储蓄银行等等。
 爱华网
爱华网