const: 用const修饰符声明的成员叫常量,是在编译期初始化并嵌入到客户端程序
static readonly: 用static readonly修饰符声明的成员依然是变量,只不过具有和常量类似的使用方法:通过类进行访问、初始化后不可以修改。但与常量不同的是这种变量是在运行期初始化。
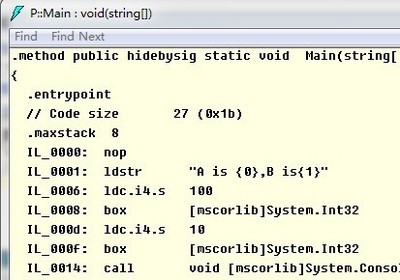
C# const和static readonly区别示例:
usingSystem; usingSystem.Collections.Generic; usingSystem.Text; namespaceExample02Lib { publicclassClass1 { publicconstStringstrConst="Const"; publicstaticreadonlyStringstrStaticReadonly="StaticReadonly"; //publicconstStringstrConst="ConstChanged"; //publicstaticreadonlyStringstrStaticReadonly="StaticReadonlyChanged"; } }
客户端代码:
usingSystem; usingSystem.Collections.Generic; usingSystem.Text; usingExample02Lib; namespaceExample02 { classProgram { staticvoidMain(string[]args) { //修改Example02中Class1的strConst初始值后,只编译Example02Lib项目 //然后到资源管理器里把新编译的Example02Lib.dll拷贝Example02.exe所在的目录,
执行Example02.exe //切不可在IDE里直接调试运行因为这会重新编译整个解决方案!! //可以看到strConst的输出没有改变,而strStaticReadonly的输出已经改变 //表明Const变量是在编译期初始化并嵌入到客户端程序,而StaticReadonly是在运行时初始化的 Console.WriteLine("strConst:{0}",Class1.strConst); Console.WriteLine("strStaticReadonly:{0}",Class1.strStaticReadonly); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
修改后的示例:
usingSystem; usingSystem.Collections.Generic; usingSystem.Text; namespaceExample02Lib { publicclassClass1 { //publicconstStringstrConst="Const"; //publicstaticreadonlyStringstrStaticReadonly="StaticReadonly"; publicconstStringstrConst="ConstChanged"; publicstaticreadonlyStringstrStaticReadonly="StaticReadonlyChanged"; } }
 爱华网
爱华网