fprintf、fscanf的读写对象不是终端而是磁盘文件;
调用方式为:intfprintf(文件指针,格式字符串,输出表列 )返回值:返回实际输出的字符数,
操作不成功返回EOF
int fscanf(文件指针,格式字符串,输入表列 )返回值:返回输入的数据个数,操作不成功返回EOF
fprintf(fp, "%d, %6.2f", i,t) 将整型变量 i 和实型变量 t的值按%d和%6.2f的格式输出到fp所指向的文件中; 若i=3,t=4.5,则输出到磁盘中的格式为:3,4.50相应的,从文件中读取数据时,则应用:fscanf(fp, "%d,%f", &i,&t)
在运用fprintf与fscanf时,在向文件输出数据及从文件读取数据时,分隔符应该相一致。如下程序所示,该程序的功能是:用户输入8个整型数据,程序回显并把数据写到int.txt文件中,然后程序再从int.txt文件中读取数据,并显示出来。
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
FILE *fp;
int i,ss[8],new[8];
for(i=0;i<8;i++){
scanf("%d",&ss[i]);
}
fp=fopen("int.txt","w");
printf("start diesplay olddata!");
for(i=0;i<8;i++){
printf("%d:%-10d",i+1,ss[i]);
fprintf(fp,"%d,",ss[i]);
}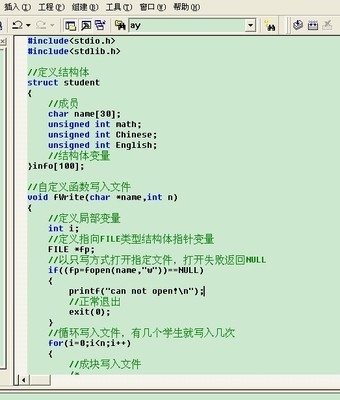
fclose(fp);
printf("Now diseplay readdate!");
if((fp=fopen("int.txt","r"))==NULL) return 1;
for(i=0;i<8;i++){
fscanf(fp,"%d,",&new[i]);
printf("%d:%-10d",i+1,new[i]);
}
fclose(fp);
}
分隔符也可采用,即回车符,那么程序中二句相应改为:
fprintf(fp,"%d",ss[i]);
fscanf(fp,"%d",&new[i]);
使用fprintf和fscanf的优点:
使用fread和fwrite的优点就是二进制的读取是最快的。但是它们有缺陷,就是在
读取的时候 while(!feof(fp)) 不精确,往往会发现它多循环了一次。因为feof
()是根据剩余字符来判断是否文件结尾的,而文件的结尾标识符是'�'是两个字
节,在读取''的时候feof()还是为false只有读取完'�'的时候feof()==true。
致使产生多余的循环(如果使用while(!feof(fp))的话)。使用fprintf和fscanf
,因为这两个函数具有输入/输出的格式限制,即使在读取'�'处有多余的循环,
但由于其不满足输入/输出格式,所以多余的循环被屏蔽掉。
最好就是这样:"%dt%dt" 这样的每个数字后面都是有限制的,这样就可以起到
很好的屏蔽作用。^^
对文件的读和写是最常用的文件操作。在C语言中提供了多种文件读写的函数:
·字符读写函数 :fgetc和fputc
·字符串读写函数:fgets和fputs
·数据块读写函数:fread和fwrite
·格式化读写函数:fscanf和fprinf
随着每次数据的读取,文件流指针fp都作相应的移动
使用以上函数都要求包含头文件stdio.h。例子都来自msdn
1 fprintf——Print formatted data to a stream
#include <stdio.h>
#include <process.h>
FILE *stream;
void main( void )
{
inti = 10;
double fp = 1.5;
char s[] ="this is a string";
char c ='';
stream = fopen("fprintf.out", "w" );
fprintf( stream, "%s%c", s, c);
fprintf( stream, "%d", i);
fprintf( stream, "%f", fp);
fclose( stream );
system( "type fprintf.out");
}
Output
this is a string101.500000
2 fscanf——Read formatted data from a stream
#include <stdio.h>FILE *stream;voidmain( void ){long l; floatfp; chars[81]; charc; stream =fopen( "fscanf.out", "w+"); if( stream== NULL)printf( "The file fscanf.out was not opened");else{fprintf( stream, "%s %ld %f %c","a-string",65000, 3.14159, 'x');fseek( stream, 0L, SEEK_SET);fscanf( stream, "%s", s);fscanf( stream, "%ld", &l);fscanf( stream, "%f", &fp);fscanf( stream, "%c", &c);printf( "%s", s);printf( "%ld", l);printf( "%f", fp);printf( "%c", c);fclose( stream);}}Outputa-string650003.141590x3 fread——Reads data from astream
4 fwrite——Writes data to a stream
读数据块函数调用的一般形式为: fread(buffer,size,count,fp); 写数据块函数调用的一般形式为:fwrite(buffer,size,count,fp); 其中: buffer是一个指针,在fread函数中,它表示存放输入数据的首地址。在fwrite函数中,它表示存放输出数据的首地址。 size表示数据块的字节数。 count 表示要读写的数据块块数。 fp 表示文件指针。
5 fgets 没有看出与fread太大的区别,除了fread可以处理string外的其他不同文件的数据类型
6 fputs
7 fgetc fputs
从键盘输入一行字符,写入一个文件,再把该文件内容读出显示在屏幕上。 #i nclude main() { FILE *fp; charch; if((fp=fopen("d:\jrzh\example\string","wt+"))==NULL) {printf("Cannot open file strike any key exit!"); getch(); exit(1);} printf("input a string:"); ch=getchar(); while (ch!='') {fputc(ch,fp); ch=getchar(); } rewind(fp); //Repositions the filepointer to the beginning of a filech=fgetc(fp); while(ch!=EOF) {putchar(ch); ch=fgetc(fp); } printf(""); fclose(fp); }
 爱华网
爱华网