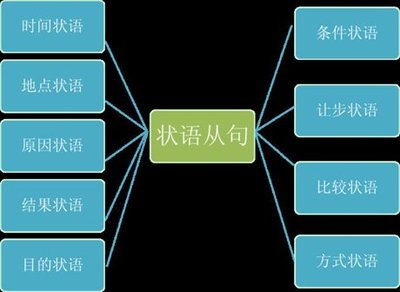
时间状语从句
在句子中起时间状语作用的句子称为时间状语从句。时间状语从句可以放在句首、句中和句尾。
引导时间状语从句的词有when,while,as,before,after,since,until/till, as soon as, once, each time, next time, the moment, immediately, instantly等。
(一)when引导的时间状语从句
1) when意为“当……时”,引导时间状语从句,表示主句的动作和从句的动作同时或先后发生。
Faith is the bird that feels the light when the dawn is still dark
信念是在黎明前的黑夜里感受到光明的鸟。
When I was wandering in the street,I met her. 我在街上徘徊的时候遇到了她。
Please tell him about it when you see him back. 你看到他回来,就告诉他这件事。
2) when引导的时间状语从句中的动词可以用延续性动词,也可以用终止性动词
He was listening to the music when I went in. 当我进去的时候,他正在听音乐。
1 will visit my parents when I have time. 我有空时会去看望我的父母。
All time is no time when it is past. 光阴一去不复返。
(二)while引导的时间状语从句
while引导的时间状语从句,常意为“与……同时,在……期间”,while引导的从句常用延续性动词或表示状态的动词。
They rushed in while we were discussing problems.
当我们正在讨论问题时,他们冲了进来。
Make hay while the sun is shining. (谚)晒草要趁太阳好。
(三)as引导的时间状语从句
as引导的时间状语从句,可以表达“正当,一边一边,随着”等意思。
1)表示某事一发生,另一事立即发生
As the sun rose the fog disappeared. 太阳一出来雾就消散了。
They strolled into the garden as the music ceased. 音乐声一停,他们就走进花园。
2)表示在某事发生的过程中另一事发生
We always sing as we walk. 我们总是边走边唱。(两个动作都是一般时态)
Just as he was speaking there was a loud explosion.
正当他在说话的时候,传来一声巨响。(从句用进行时态)
3)表示两个动作同时发生
As she sang,tears ran down her cheeks. 她一边唱歌,眼泪一边从脸颊淌下。
He smiled as he passed. 他路过的时候笑了一下。
He saw that she was smiling as she read. 他看到她一边看书一边笑。
We get wiser as we get older.
我们随着年龄的增长而变得聪明起来。(随时间的变化而变化)
(四)before引导的时间状语从句
before意为“在……之前”,引导时间状语从句时,表示主句的动作发生在从句的动作之前。
Before I could get in a word, he already gave orders.
我还来不及插话,他已经吩咐下去了。
Mr. Brown had worked in a bank for a year before he came here.
布朗先生来这之前已经在一家银行里工作一年了。
It was two years before we met again. 两年后我们才再次见面。
It will not be long before you regret for what you've done.
不久你就会为你的所作所为后悔的。
(五)after引导的时间状语从句
after意为“在……之后”,引导时间状语从句时,表示主句的动作发生在从句的动作之后。
After you use plastic bags, you mustn't throw them about.
用完塑料袋后,不准到处乱扔。
Please let me know your decision after you have thought it over.
在你仔细考虑过之后请告诉我你的决定。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:若主句和从句两个动作发生的先后顺序十分接近,那么也可以不用完成时态,例如上面的第二句可改成: Please let me know your decision after you think it over.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(六)since引导的时间状语从句
此时since常意为“自从……”,主句常用现在完成时,从句常用一般过去时。
We have made many dumplings .since we began to cook.
自从我们开始做饭起,我们已经包了许多饺子了。
In the 12 months .since I last wrote to you, a lot has happened to me.
自从上次我给你写信以来的一年里,我经历了许多事。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:常用句型:it is/has been+时间段+since从句常译为“自从……有多长时间了“。
It’s been years since I enjoyed myself so much. 我已经很多年没有那么痛快了。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(七)until/till引导的时间状语从句
until/ till意为“直到……时”,引导时间状语从句时,表示主句的动作发生在从句的动作之前。当主句的谓语动词是持续性动词时,主句常用肯定形式;当主句的谓语动词是非持续性动词时,主句常用否定形式,not…until… 意为“直到……才……”,这时的until可以用before来替换。
I'll stay here until you come back.
我会待在这里,直到你回来。(stay表示的动作可以持续)
He didn’t leave home until his father came back.
他直到父亲回家才离开。(leave home 表示的动作不能持续)
Please wait until I arrived.请在我到达之前等着我。(wait表示的动作可以持续)
(八)as soon as引导的时间状语从句
as soon as意为“一……就……”,表示从句的动作一发生,主句的动作马上就发生。
The boy run to the cinema as soon as his father went out.
他的父亲一出去,男孩就跑去电影院了。
As soon as I reach Canada.1 will ring you up. 我一到加拿大,就给你打电话。
(九)once引导的时间状语从句
once引导的时问状语从句暗含条件意味,意为“一旦……就……”。
Once you begin, you must go on. 一旦你开始了,就要继续下去。
Once having made a promise, you should keep it.一旦许诺,就要遵守。
Math is easy to learn once you understand the rules.
一旦你理解了这些定律,数学就不难学了。
(十)名词短语引导的时间状语从句
名词短语the moment,the minute, the instant, the time, the hour, the day, by the time, each time, every time, next time, any time等也可引导时间状语从句。
The moment I saw him, I knew there was still hope.
我一看到他就知道还有希望。
Every time I saw the straw hat, it reminded me of the tour I made years ago.
每当我看到那顶草帽,就使我想起几年前的那次旅游。
I thought it is beautiful and clean the first time I arrived the city.
我第一次来到这座城市就觉得它很漂亮很干净。
He was much better the last time I saw him. 上次我见到他,他好多了。
By the time you came back, I had finished this book.
到你回来时,我已经写完这本书了。
(十一)其他连词引导的时间状语从句
Immediately, instantly, directly引导时间状语从句。
Directly the master came in, everyone was quiet. 校长一进来,大家就安静下来。
Make sure the property you are buying is insured immediately you exchange contracts. 交换合同,就应立刻给所购房产买保险。
Directly you feel any pains, you must go to see the doctor. 你一感觉不舒适就找医生。
Please write to me instantly you arrive. 你一到就给我写信。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:no sooner…than…, hardly/scarcely/barely…when…引导的表示时间的句子,主句在前面,从句用一般过去时,主句用过去完成时。 ┃
No sooner had the sun shown itself above the horizon than he got out of bed to commence work. 太阳刚从地平线上升起,他就起床劳动去了。
=The sun had no sooner shown itself above the horizon than he got out of bed to commence work.
Hardly had I explained the reason to him when he stopped listening.
我还没来得及向他解释原因,他就不听了。
=I had hardly told him the reason when he stopped listening.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
地点状语从句
在句中作地点状语的从句称为地点状语从句,常由where,wherever,anywhere,
everywhere,nowhere等引导。地点状语从句可置于句首、句中或句尾。
Wherever I am l will be thinking of you. 不管在哪里我都会想你的。
Let's go wherever this path will take us. 我们就顺着这条小路走,走到哪儿就算哪儿。
Where there is life, there is hope.(谚)一息尚存,希望不灭。
Where there is a will, there is a way.(谚)有志者,事竞成。
Just stay there you are and don't move. 呆在你现在呆的地方别动。
You should have put the book where you found it.你本来应该把书放回原来的地方。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:where引导的地点状语从句一般可以转化为定语从句,只要在where前加上to/in/from the place, to/in/from places或to/in/from any place等构成to/in/from/the place where或to/in/from any place where,便可变成定语从句。
上面带有地点状语从句的最后两个例句可改为下面带有定语从句的句子,意思不变:
Just stay in the place where you are and don’t move.
You should have put the book in the place where you found it.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
原因状语从句
在句中作原因状语的从句称为原因状语从句。原因状语从句可置于句首,也可置于句尾。引导原因状语从句的常用词可分为两类:单词引导词和短语引导词。单词引导词主要有because, since, as等;短语引导词主要有now that, seeing that, for the reason that, in that, considering (that)等。
(一)because引导的原因状语从句
表因果关系的语气最强,用来回答以why提问的问句,所引出的原因往往是听话人所不知道或最感兴趣的。because引导的原因状语从句往往比主句显得更重要。
Man's real life is happy, chiefly because he is ever expecting that it soon will be so.
人的现实生活是幸福的,主要是因为他总是期望生活不久将会幸福。
Big goals are necessary because you must see it big before you can make it big.
远大的目标是必要的,因为你在实现远大的目标之前.必须视其为远大的目标。
He is absent today because he is ill. 因为他病了,所以今天没来。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:在主句是否定的情况下,because从句的理解有两种情形,需要根据上下文进行综合理解。
I did not buy the pen because it's cheap.
我没有买这支笔,因为便宜。/我不是因为便宜才买了这只笔。
I didn't buy the pen, because it's cheap.我没买这只笔,因为它便宜。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(二)since引导的原因状语从句
表示人们已知的事实,不需强调的原因,故常译成“既然……”,通常放在句首。since引导的从句是次要的,重点强调主句的内容。
Since you are so sure of it, he'll believe you.
既然你对此如此有把握,他会相信你的。
Since tomorrow is Jim's birthday, let's give him a party.
既然明天是吉姆的生日,咱们举行一个宴会吧。
Since we cannot be universal and know all that is to be known of everything, we ought to know a little about everything. 既然我们不能万事皆通,不能通晓可以了
解的每一事物的一切,我们应当对每一事物都有所了解。
(三)as引导的原因状语从句
as与since用法差不多,所引出的理由在说话人看来已经很明显,或已为听话人所熟悉而不须用because加以强调。as引导的从句与主句具有同等的地位。
We have to delay our journey, as the weather is so bad.
因为天气太恶劣了,我们要推迟我们的行程。
As rain has fallen,the air is cooler. 因为下过雨,空气比较清爽。
I left a message as you weren't there.你没在,我就给你留了字条。
I have to speak English with them, as the guys I live with don't know any Chinese.
和我生活在一起的那些人不懂汉语,我只好同他们说英语。
(四)其他连词引导的原因状语从句
另外now that,seeing that,for the reason that,in that,considering( that)等也可引导原因状语从句。
Now that they've got to know each other a little better, they get along just fine.
由于彼此之间有了进一步了解,他们相处得不错。
Seeing (that) he is inexperienced, he is not fit for the work.
贶然他没有经验,他就不适合这项工作。
I often go to the cinema for the simple reason that I love seeing film.
我经常去电影院,原因很简单,那就是我喜欢看电影。
1 like the city, but I prefer the country in that there's fresher air.
我喜欢城市,但我更喜欢乡村,因为那里有更清新的空气。
Considering (that) he hasn't fully recovered yet, it will not be proper to assign him such a hard job.考虑到他身体还没有完全恢复,指派他干这样的难活不适宜。
目的状语从句
在句中作目的状语的从句称为目的状语从句。目的状语从句可置于句首、句中或句尾。常用来引导目的状语从句的关联词有:so, so that, in order that, for fear in case (that), for the purpose that, lest等。
(一)in order that,so that引导的目的状语从句
in order that带用于正式文体,可置于句首,也可置于句尾,而so that往往只置于句尾,但也有置于句首的,so that短语中有时可省略that。
We shall let you know the details soon so that /in order that you can/may make your arrangements. 不久我们将会让你知道详情,以便你们能够做出安排。
I opened the window so that fresh air might come in.
我把窗户打开以便新鲜空气可以进来。
I've decided to learn photography in order that I may record the beauty of nature. 我决定学摄影以便能记录大自然的美。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:省略后的不定式in order to do/so as to do(逻辑主语相同)或in order for sb.
to do(逻辑主语不同)也可引导目的状语从句,上面三个例句可改为:
We shall let you know the details soon in order for you to make your arrangements. I opened the window in order for fresh air to come in.
I've decided to learn photography in order to record the beauty of nature.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(二)for fear(that), in case, lest引导的目的状语从句
for fear (that)表示目的时,意为“唯恐,以防”, in case意为“目的是,以防,以免,以防有某种情况发生”,lest意为“以防”。这三个短语或词都相当于in order that…not.... ,so that…not…。
Shut out the window lest/in case it should rain. 关上窗以防下雨。
The victims all seemed afraid to say the facts, for fear it might start trouble.
受害人似乎都不敢说出真相,怕引起麻烦。
She hid away from the window lest anyone see her.
她从窗口躲开了,免得有人见到她。
I stayed all day at home in case (that) you called.
我整天待在家里以防你打电话。
She is studying hard for fear that she should lag behind others.
她学习很刻苦,唯恐落在别人后面。
结果状语
在句子中作结果状语的从句称为结果状语从句。结果状语从句一般置于句尾。常用来引导结果状语的引导词或短语有:so, so that, so...that…, such that, such…that…, that等。
(一)so that与so…that…引导的结果状语从句
so that/so…that…引导结果状语从句,意为“如此……以至于”,在口语中,that常可省略。
1)so that引导的结果状语从句
In his fury he threw the vase upon the ground so (that) they were broken.
他盛怒之下,便把花瓶扔到地上,摔破了。
We moved to the country so that we were away from the noisy and dull city.
我们搬到了乡下,所以我们远离了吵闹、单调的城市。
She is ill so that she can't attend the meeting this afternoon.
她病了,不能参加今天下午的会议了。
2) so…that…引导的结果状语从句
so…that…引导结果状语从句可以构成如下结构:
形容词/副词
many/few(+可数名词的复数)
much/little(+不可数名词)
形容词+a/an+可数名词单数
动词
so+ +(that)+从句
Mike is so honest a man that we all believe him.
麦克是如此诚实的一个人,以至于大家都相信他。
I've had so many falls that I'm black and blue all over.
我跌了很多跤,浑身摔得青一块紫一块。
Lily left home so hurriedly that she left her documents home.
莉莉出门时太匆忙,结果将文件都忘在家里了。
He was so benevolent, so merciful a man that he would have held an umbrella over a duck in a shower of rain. (谚)他是那么大慈大悲,会在倾盆大雨中给鸭子打伞。
(二)such(…)that…引导的结果状语从句
such(…)that…引导结果状语从句,可以构成如下结构:
a/an+形容词十可数名词单数
such+ 形容词十可数名词复数 +(that)+从句
形容词十不可数名词
It is such nice weather that I'd like to take a walk.
天气是如此之好,以至于我想去散散步。
Kathy is such a young girl that she can't go to school.
凯茜年龄太小了,还不能去上学。
These were such difficult questions that none of us could answer.
这些问题如此难,以致我们没人能回答。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:so/such引导的结果状语从句放于句首时,主句的助动词要置于主语前面。为了强调形容词或副词,so…that…引导的结果状语从句,可把so置于句首,主句用倒装语序。
So excited was he that he could not fall into sleep.他太激动了不能入睡。
Such was his worry that he couldn't go on his work.
他如此担忧以致不能继续上班
So carelessly did he drive that he nearly got killed. 他开车如此粗心差点遇难。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(三)that引导的结果状语从句
What has Tom done that you should be so worried about him?
汤姆做了什么让你这么担忧?
Kate is conceited that we all don't want to work together with her.
凯特如此自负,我们都不想和她一起丁作。
The question is of great importance that it cannot be neglected.
这个问题很重要,不容忽视。
条件状语从句
在句子中作条件状语的从句称为条件状语从句。条件状语从句可置于句首,也可置于句尾,有时还可置于主语和谓语之问。引导条件状语从句的常用引导词为:if,unless, as/so long as, once, in case, on condition that, supposing (that), providing (that),provided (that),given (that)等。在条件状语从句中,一般要用一般现在时表示一般将来时,一般过去时表示过去将来时.现在完成时表示将来完成时。
(一)if引导的条件状语从句
if是引导条件状语从句最常用的连词,表示在某种条件下某事很可能发生。
If you heat ice,it melts. 如果你给冰加热,它会融化。
If you do not learn to think when you are young, you may never learn.
如果年轻时不学会思考,你也许永远不会思考。
If we command our wealth, we shall be rich and free; if our wealth commands us,we are poor indeed.
如果我们支配财富,就会富裕而自由,如果我们为财富所支配,就是真的贫穷。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:if 从句还表示不可实现的条件或根本不可能存在的条件,也就是一种虚拟的条件或假设,从句多用一般过去时或过去完成时。条件状语从句分为真实条件状语从句和非真实条件状语从句。
If I were you , I wouldn't invite him to the party.
如果我是你,我不会邀请他参加聚会。
The flower would not have died if I had watered them before I left home.
如果我在离开家之前浇了水,这些花就不会死了。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(二)unless引导的条件状语从句
Unless意为“除非,若不,除非在……的时候“。
Victory won't come to us unless we go to it.
胜利不会走向我们,我们必须自己走向胜利。
Courage is doing what you are afraid to do, There can be no courage unless you are scared.
勇气就是去干你所畏惧的事情。只有当你胆怯时才有勇气可言。
unless it rains, the game will be played. 除非下雨,比赛将照常进行。
I shall go there tomorrow unless I'm too busy. 如果我不太忙,明天将到那儿去。
Unless I am mistaken, I've seen that man before.
如果我没搞错,我以前见过那个人。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:unless的意识相当于if…not…。上面的最后两个例句可变为:
I shall go there tomorrow, if I am not too busy.
If I am not mistaken, I have seen that man before.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(三)on condition(that).引导的条件状语从句
on condition(that).引导的条件从句是主句事件发生的前提条件或唯一条件,意为”在……条件下”。
I can tell you the truth on condition that you promise to keep secret.
我可以告诉你真相,条件是你答应保守秘密。
Ron lent me the money on condition that I pay it back next month.
岁恩把钱借给我,条件是下月归还。
I will go with you on condition that you buy me a new bicycle.
只要你给我买一辆新白行车,我就跟你去。
(四)supposing/provided/providing/given(that)引导的条件状语从句
supposing/providing/provided(that)可以用做连词,意为“如果”,引导的条件从句表示一种假设条件。这几个词意义相近。
Supposing (that) it rains, shall we continue the sports meeting?
倘若下雨,我们的运动会还要继续举行吗?
Supposing (that) something should go wrong, what would you do then?
假如出了什么问题,你准备怎么对付?
It's not worth the risk, supposing your mother found out.
不值得冒这个险,万一你妈妈发现了怎么办?
I don't mind Guy coming with us. Provided/providing (that) he pays for his own meals. 只要盖伊自付餐费,我不介意他和我们一起去。
I will cooperate provided/providing (that) I am notified on time.
只要及时告诉我,我就会合作。
Providing /Supposing/Given/Provided (that) you promise not to tell anyone else, I'll explain the secret. 只要你保证不告诉任何人,我就把这个秘密告诉你。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:in case 在英式英语中表示目的,在美式英语中可表示条件,意为“如果,万一“。
In case I am late, start without me. 要是我来晚了,你们就先开始吧。
Take a hat with you in case the sun is very hot.
随身带着帽子,以防阳光太烈。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
让步状语从句
在句中充当让步状语的从句称为让步状语从句。让步状语从句既可置于主句之前,也可置于主句之后。引导让步状语从句的连词有although,though,even if.Even though, if, when, whether…or…, whether(…) or not, while, whatever, no matter what/how/why等。
(一)though/although的用法
although和though意义一样,都作“虽然,即使”解,都表示让步,一般情况下可互换使用,只是although语气较重,大多置于句首。though/although引导让步状语从句时,主句若用yet或still引出,更加强调对比性,但不可出现but。有时也用倒装句型。在as though,even though中一般不可用although代替。同时although不可当副词用,而though可以。
They are generous though they are poor. 虽然他们很穷,但他们很慷慨。
Although we have grown up, our parents still treat us as children.
尽管我们已经长大了,可是我们的父母仍把我们看做小孩。
Although he is rich,yet he is not happy. 虽然他很富有,但是他并不快乐。
Though a lie may be well dressed, it is ever overcome.
即使谎言被修饰地再好,到头来总会被揭穿。
(二)even though/even if引导的让步状语从句
这两个短语表示语气更强的让步,常常意为“再退一步说”。even though更加强调对“既成事实”的让步,even if更强调对“假设”的让步。
I'll get there even if /even though I have to walk all the way.
即使得一路走着去,我也要走到那里。
Even if he is poor, she loves him. 即使他很穷,但她还是爱他。
=He may be poor, yet she loves him.
Even though he is poor, she loves him.尽管他很穷,但她还是爱他。
=He is poor, yet she loves him.
(三)as引导的让步状语从句
as表示“让步”时常用倒装。倒装时若有带冠词的名词,冠词需要省去。as的这种用法与though倒装时的用法完全一致,although不可这样用。as引导的让步状语从句必须以部分倒装的形式出现,被倒装的部分可以是表语、状语或动词原形。
Urgent as/though the message is, it is impossible to send it there in time.
消息很紧急,但不可能及时送到。
=Though the message is urgent, it is impossible to send it there in time.
Child as/though he was, he faced the dangerous situation calmly.
尽管还是个孩子,但他能冷静地面对危险情况。
=Though he was a child, he faced the dangerous situation calmly.
Much as he loves his daughter, he is strict with her.
仡很爱女儿,但对她管教也很严。
Reject as you may,I'll go. 纵使你反对,我也要去。
=Though/Although you may reject, I'll go.
(四)whether…or…/whether(…)or not引导的让步状语从句
whether…or…/whether(...)or not表示“不论是否……”,“不管是……还是……”之意。由这一个复合连词引导的让步状语从句旨在说明正反两个方面的可能性都不会影响主句的意向或结果。
I'll go, whether you come with me or stay at home.
不论你来还是留在家中,我都要去。
Whether you believe it or not, it is true. 无论你是否相信,这都是真的。
I'll marry her whether she is poor or rich. 不管她是穷还是富我都要和她结婚。
(五)while引导的让步状语从句
while也可以引导让步状语从句,表示“尽管(部分承认……是事实)”,比though/
although语气弱。while引寻的让步状语从句一般要位于句首。
While she is a lovely girl, she can be extremely difficult to work with.
她虽然是一个可爱的姑娘,但有时很难与她共事。
While I understand what you say, I can't agree with you.
虽然我理解你的意思,但我还是不同意。
(六)wh-ever类词引导的让步状语从句
在英语中,wh-ever类词可作主句的疑问词,也可引导名词性从句,还可引导让步状语从句。一般没有whyever的用法,同时whether本身就代替了whetherever的形式。这类词在引导让步状语从句时常可换成no matter+相应的wh-词,在引导名词性从句时只能用wh-ever。
Whatever you say, I won't believe you. 无论你说什么,我都不会相信。
=No matter what you say, I won't believe you.
Whenever I'm unhappy, it is my friend who cheers me up.
不管什么时候我不高兴,总是我的朋友使我振作起来。
=No matter when I'm unhappy, it is my friend who cheers me up.
I'll wait for you however late it is.不管有多晚我都会等着你。
=I'll wait for you, no matter how late it is.
Whoever wants to speak to me on the telephone, tell him I'm busy.
不管谁打电话找我,告诉他我很忙。
=No matter who wants to speak to me on the telephone, tell him I'm busy.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:“no matter+疑问句”结构只能引导让步状语从句,而wh-ever类词还可以引导名词性从句。
Whatever(=No matter what) happened, he would not mind.
(让步状语从句)无论发生什么,他都不会介意。
I will take whoever (≠no matter who )wants to go. 谁想去我就带谁去。
Whoever(≠No matter who )comes will be welcome.
(主语从句)不管谁来都会受到欢迎。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
比较状语从句
在句子中作比较状语的从句称为比较状语从句。比较状语从句一般位于句尾。
比较状语从句常用as…as, not as/so…as...,than等连接词引导。“the+比较级…; the+比较级…”结构也可引导比较状语从句。
(一)同级比较
同级比较常用;as…as…结构。
They want peace as much as we do. 他们和我们一样都需要和平。
Is it as good as you expected? 它有你期待的那样好吗?
She is as bad-temper as her mother (is). 她和她妈妈一样脾气很坏。
Water is eight hundred times as dense as air (is). 水的密度是空气密度的八百倍。
(二)不同级比较
不同级比较常用not as/so…as...结构。
I can't run as fast as I used to. 我不如过去跑得快了。
I am not so young as you think. 我没有你想的那么年轻。
Nothing is so popular as goodness.(谚)最受欢迎的是善行。
(三)差级或高级比较
差级或高级比较常用…than…结构。
I like the dreams of the future than the history of the past.
与过去的历史相比,我更喜欢未来的梦想。
If I have made any valuable discoveries, it has been owing more to patient attention than to any other talent.
如果说我有什么重要的发现,与其说这归功于我的天赋和才华,倒不如说是因为我持之以恒的专注。
A valiant man's look is more than a coward's sword.
(谚)勇士的目光比懦夫的剑更锋利。
(四)比较关系的状语从句
比较关系的状语从句常用结构为“the+比较级… ,the+比较级…”。
The more we do, the more we can do; the busier we are, the more leisure.
找们做得越多,能做的就越多;越是紧张,就越有闲暇。
The miracle is this---the more we share, the more we have.
神奇的是我们分享的越多,我们拥有的也越多。
The harder you work,the more progress you will make.你越用功,进步就会越大。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:what/as 也可引导对称或对比关系的状语从句。
Food is to men what/as oil is to machine.食物之于人犹如油之于机器。
Engines are to machines what/as hearts are to animals.
引擎对于机器就好比心脏对于动物一样。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
方式状语从句
在句子中作方式状语的从句称为方式状语从句。方式状语从句一般位于句尾,有时位于句中。常用连接词as,(just) as…so...,as if,as though,the way等引导。
(一)as if/as though引导的方式状语从句
两者的意义和用法相同,引出的状语从句谓语多用虚拟语气,表示与事实相反,有时也用陈述语气,表示所说情况是事实或实现的可能性较大。常意为“仿佛……似的,好像……似的”。
I remember the whole thing as if it happened yesterday.
我记得整件事情,就仿佛是昨天发生的一样。(与事实相反,谓语用陈述语气)
It looks as if the weather may pick up very soon.
看来天气很快就会好起来。(实现的可能性较大,谓语用陈述语气)
(二)as,(just)as…so…引导的方式状语从句
as, (just) as…so…等引导的方式状语从句通常位于主句后。(just) as…so…结构位于句首时, as从句带有比喻的含义,意为“正如……,就像”,多用于正式文体。
Always do to the others as you would be done by.
你希望人家怎样待你,你就要怎样待人。
When in Rome do as the Romans do. (谚)入乡随俗。
Leave the children as they are. 让孩子们自由随便,不要管他们。
As water is to fish,as air is to man. 我们离不开空气,犹如鱼儿离不开水。
Just as we sweep our rooms, so we should sweep backward ideas from our minds. 正如打扫房屋一样,我们也要扫除我们头脑中落后的东西。
状语从句中的省略
在表示时间、地点、条件、方式(比较)或让步等的状语从句中,如果谓语含有动词be,主语又和主句的主语一致,或其主语是it,那么从句中的主语和谓语的一部分(尤其是be动词)往往可以省略。使用这些省略结构可收到言简意赅之功效。
(一)从属连词+名词
Though (he was) a young man, he has written three famous novels.
虽然还是个年轻人,他已经写了3本著名的小说了。
When (he was) still a boy of six, Bob was sent away from home.
鲍勃才六岁时就被送出家门。
As (she was) a child she began to learn to play the piano.
还是个孩子时,她就开始学习弹钢琴。
(二)从属连词+形容词
When (they are) ripe, the grapes will be delicious.当葡萄成熟之后就会很好吃。
Though (she was) young, she had to live on herself.
虽然年纪轻轻,但她不得不养活自己。
He talked to the stranger as if (he were) absent-minded.
他和陌生人谈话似乎很不在意。
He is a good man, though sometimes (he is) rather dull.
他真是个好人,尽管有时有点无聊。
(三)从属连词+副词
Once(you are)inside,begin to work. 一就绪,就开始工作。
Unless (you are) here, you can't find this kind of butterflies.
除非在这里,其他地方找不到这种蝴蝶。
While (we were) there, we joined in voluntary labor on a project.
我们一到那儿,就自愿参加了这项工程。
(四)从属连词+介词短语
When (you are) in doubt, please consult a dictionary.
有疑问的时候,就请查字典。
The waves dashed on the rocks as if (they were) in anger.
波涛冲击着岩石,好像发怒一般。
She looked anxious as though (she was) in trouble.
她看上去很焦急,好像遇到了麻烦。
While (I was) at college, I began to know him, a strange but capable student.
我在上大学时就开始认识他,他是一个奇怪但有能力的学生。
He opened the desk, as if (he was) in search of something important.
他打开抽屉好像在找一件什么重要的东西。
(五)从属连词+不定式
She moved his lips as if (she wanted) to speak. 她的嘴动着仿佛要说什么。
He raised his hand as if (he were) to ask something. 他举起手好像要问什么。
He wouldn't solve the problem even if (he were) to take charge.
即使他来负责,他也解决不了这个问题。
He cleared his throat as if (he wanted), to say something.
他清了清嗓子,像要说什么似的。
(六)从属连词+动词的-ing形式
Look out for cars when (you are) crossing the street. 过马路时要小心。
Though lacking money, his parents managed to send him to university.
虽然他的父母缺钱,他们仍把他送入了大学。
=Though his parents lack money, they managed to send him to university.
He stared at me as if seeing me for the first time.
他目不转睛地看着我,就像第一次看见我似的。
=He stared at me as if he had seen me for the first time.
The boy is running impatiently here and there as if (he is) searching for something lost on the sports ground.
这男孩很不耐烦地在操场上到处跑着,仿佛在找什么东西。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
注意:as在引导时间状语从句时,气候不能运用省略形式,此时用when, while替代。
When/While living in London, I picked up English. (不能用as)
在伦敦期间我学了英语。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(七)从属连词+动词的-ed形式
When (it is) taken according to the directions, the drug has no side effects.
按照说明服用,这种药就没有副作用。
When (it is) published, the novel will become one of the best sellers of the year.
一旦出版,这部小说将会成为该年度的畅销书之一。
She has finished the work earlier than (it has been) expected.
她这项工作比预期的提前完成。
Even if (I am) invited to, I won't go to such a bad concert.
即使邀请我去,我都不想去听如此差的音乐会。
You should stay where you are, unless (you are) asked to leave.
除非叫你离开,否则你应待在原地。
The boy wouldn't leave even though (he had been) asked to twice.
尽管给小男孩说过两次,但他还是不愿离开。
(八)其他形式
1) 省略式的条件状语从句句型为if necessary,if possible, if true,if so, if not, if anyone, unless, once, as long as等词或短语后也运用省略形式。这种省略式的状语运用频繁,有的已经成了习惯表达法,被人们所熟知,而对于其完整的状语从句用的越来越少。
If (it is) necessary, we will buy a new car.
如果有必要的话,我们会买一辆新车。
If (it is) possible, I'll travel to Denmark next month.
如果可能的话,下个月我会去丹麦旅行。
He may be busy,if (it is) so, I'll call later. If (it is) not, can I see him now?
他可能很忙,要是这样,我以后再来拜访。要是不忙,我现在可以见他吗?
If (it is) true, this will cause us a lot of trouble.
如果是真的,这会给我们带来很多麻烦。
There are few people nowadays, if (there are) any, who remember him.
现在很少有人能记起他。
2) 状语从句中的主语尽管与主句的主语不相同,但如果它与主句的逻辑主语相同或根据主、从句的对应关系判断,意思比较明确,同时,从句的谓语又含有动词“be"的某种形式,则可省略从句中的“主语+be"部分。
There are a few simple safety measures to follow while (you are) training.
有几点简单的安全措施训练时必须遵守。
We all expect to live where (the place is) not polluted.
我们每个人都期望生活在一个未受到污染的地方。
3) 如果状语从句和主句都含有“there be”的某种形式或只有状语从句含有“there be”的某种形式,从句中的“there be'’常常也可以省略
There are few, if (there are) any mistakes in that book.
那本书就是有错误也不多。
We shouldn't lose heart as long as (there is) any hope with us.
只要有一线希望我们就不能灰心。
4) 由than和as引导的比较状语从句,在意义明确的情况下,可省略than和as后面
的任何部分
He works as fast as a skilled worker (does).他工作起来和技术工人一样快。
I know you better than (I know) him. 我对你比对他了解得清楚。
I know you better than he (knows you). 我比他更了解你。
In winter it's colder in Beijing than (it is cold) in Guangzhou.
在冬天,北京比广州冷。
自测习题
1. I am going to pursue this course,________________________________________(无论我要做出什么样的牺牲).
2. I would prefer shopping online to shopping in a department store because______________________________________(它更方便和省时).
3. The matter was so serious that I____________________________________(除了报警别无选择).
4. She is said to have been a good student until she______________________________(在期末考试中被抓住作弊).
5. If you had_______________________________________(听从了我的忠告,你就不会陷入麻烦).
6. The farmer put up iron fences around the garden _____________________________(以免邻居家的羊闯进来).
7. ________________________________________(如果这所大学没有这么好的声誉), I would not have come here.
8. _________________________________________(尽管他要达到父母的期望很难),he was determined to do his best.
9. __________________________________(当他的公司处于破产边缘的时候),one of his customers gave him an order.
10. you can start your own business____________________________________(只要得到当局允许).
11. __________________________________________(为了确保这个制度同过去一样卓有成效),we must root out fraud and abuse.
 爱华网
爱华网


