一、实验名称
数据结构哈夫曼树的应用
二、问题描述
利用赫夫曼编码进行通信可以大大提高信道利用率,缩短信息传输时间,降低传输成本。这要求在发送端通过一个编码系统对待传输数据预先编码,在接收端将传来的数据进行译码(复原)。对于双工信道(即可以双向传输信息的信道),每端都需要一个完整的编/译码系统。试为这样的信息收发站编写一个赫夫曼码的编/译码系统。
三、基本要求
一个完整的系统应具有以下功能:
(1)I:初始化(Initialization)。从终端读入字符集大小n,以及n个字符和n个权值,建立赫夫曼树,并将它存于文件hfmTree中。
(2)E:编码(Encoding)。利用已建好的赫夫曼树(如不在内存,则从文件hfmTree中读入),对文件ToBeTran中的正文进行编码,然后将结果存入文件CodeFile中。
(3)D:译码(Decoding)。利用已建好的赫夫曼树将文件CodeFile中的代码进行译码,结果存入文件Textfile中。
以下为选作:
(4)P:印代码文件(Print)。将文件CodeFile以紧凑格式显示在终端上,每行50个代码。同时将此字符形式的编码文件写入文件CodePrin中。
(5)T:印赫夫曼树(Treeprinting)。将已在内存中的赫夫曼树以直观的方式(比如树)显示在终端上,同时将此字符形式的赫夫曼树写入文件TreePrint中。
四、测试要求
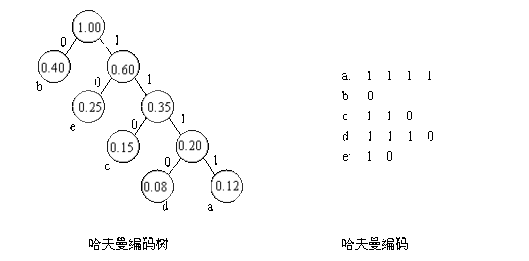
(1)已知某系统在通信联络中只可能出现八种字符,其频率分别为0.05,0.29,0.07,0.08,0.14,0.23,0.03,0.11,试设计赫夫曼编码。
(2)用下表给出的字符集和频度的实际统计数据建立赫夫曼树,并实现以下报文的编码和译码:“THISPROGRAMEISMYFAVORITE”。
字符 | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | |
频度 | 186 | 64 | 13  | 22 | 32 | 103 | 21 | 15 | 47 | 57 | 1 | 5 | 32 | 20 |
字符 | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | |
频度 | 57 | 63 | 15 | 1 | 48 | 51 | 80 | 23 | 8 | 18 | 1 | 16 | 1 |
(3)编码结果以文本方式存储在文件Codefile中。
(4)用户界面可以设计为“菜单”方式:显示上述功能符号,再加上“Q”,表示退出运行Quit。请用户键入一个选择功能符。此功能执行完毕后再显示此菜单,直至某次用户选择了“Q”为止。
(5)在程序的一次执行过程中,第一次执行I,D或C命令之后,赫夫曼树已经在内存了,不必再读入。每次执行中不一定执行I命令,因为文件hfmTree可能早已建好。
五、源代码/数据测试
#include<iostream.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<fstream.h>
typedefstruct{//赫夫曼树的结构体
charch;
intweight;//权值
intparent,lchild,rchild;
}htnode,*hfmtree;
typedefchar**hfmcode;
voidSelect(hfmtree&HT,inta,int*p1,int*p2)//Select函数,选出HT树到a为止,权值最小且parent为0的2个节点
{
inti,j,x,y;
for(j=1;j<=a;++j){
if(HT[j].parent==0){
x=j;
break;
}
}
for(i=j+1;i<=a;++i){
if(HT[i].weight<HT[x].weight&&HT[i].parent==0){
x=i;//选出最小的节点
}
}
for(j=1;j<=a;++j) {
if(HT[j].parent==0&&x!=j)
{
y=j;
break;
}
}
for(i=j+1;i<=a;++i)
{
if(HT[i].weight<HT[y].weight&&HT[i].parent==0&&x!=i)
{
y=i;//选出次小的节点
}
}
if(x>y){
*p1=y;
*p2=x;
}
else
{
*p1=x;
*p2=y;
}
}
voidhfmcoding(hfmtree&HT,hfmcode&HC,intn)//构建赫夫曼树HT,并求出n个字符的赫夫曼编码HC
{
inti,start,c,f,m,w;
intp1,p2;
char*cd,z;
if(n<=1){
return;
}
m=2*n-1;
HT=(hfmtree)malloc((m+1)*sizeof(htnode));
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)//初始化n个叶子结点
{
printf("请输入第%d字符信息和权值:",i);
scanf("%c%d",&z,&w);
while(getchar()!='n')
{
continue;
}
HT[i].ch=z;
HT[i].weight=w;
HT[i].parent=0;
HT[i].lchild=0;
HT[i].rchild=0;
}
for(;i<=m;++i)//初始化其余的结点
{
HT[i].ch='0';
HT[i].weight=0;
HT[i].parent=0;
HT[i].lchild=0;
HT[i].rchild=0;
}
for(i=n+1;i<=m;++i)//建立赫夫曼树
{
Select(HT,i-1,&p1,&p2);
HT[p1].parent=i;HT[p2].parent=i;
HT[i].lchild=p1;HT[i].rchild=p2;
HT[i].weight=HT[p1].weight+HT[p2].weight;
}
HC=(hfmcode)malloc((n+1)*sizeof(char*));
cd=(char*)malloc(n*sizeof(char));
cd[n-1]='�';
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)//给n个字符编码
{
start=n-1;
for(c=i,f=HT[i].parent;f!=0;c=f,f=HT[f].parent)
{
if(HT[f].lchild==c)
{
cd[--start]='0';
}
else
{
cd[--start]='1';
}
}
HC[i]=(char*)malloc((n-start)*sizeof(char));
strcpy(HC[i],&cd[start]);
}
free(cd);
}
intmain(){
charcode[100],h[100],hl[100];
intn,i,j,k,l;
ifstreaminput_file;//文件输入输出流
ofstreamoutput_file;
charchoice,str[100];
hfmtreeHT;
hfmcodeHC;
cout<<"n";
cout<<""<<"计算机(3)班"<<""<<"n";
while(choice!='Q'&&choice!='q')//当choice的值不为q且不为Q时循环
{
cout<<""<<"*************************赫夫曼编码/译码器*************************n";
cout<<""<<"I.Init"<<""<<"E.Encoding"<<""<<"D.Decoding"<<""<<"Q.Exitn";
cout<<"请输入您要操作的步骤:";
cin>>choice;
if(choice=='I'||choice=='i')//初始化赫夫曼树
{
cout<<"请输入字符个数:";
cin>>n;
hfmcoding(HT,HC,n);
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
cout<<HT[i].ch<<":"<<HC[i]<<endl;
}
output_file.open("hfmTree.txt");
if(!output_file){
cout<<"can'toenfile!"<<endl;
return1;
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
output_file<<"("<<HT[i].ch<<HC [i]<<")";
}
output_file.close();
cout<<"赫夫曼树已经创建完毕,并且已经放入hfmTree.txt文件中!"<<endl;
}
elseif(choice=='E'||choice=='e')//进行编码,并将字符放入ToBeTran.txt,码值放入CodeFile.txt中
{
printf("请输入字符:");
gets(str);
output_file.open("ToBeTran.txt");
if(!output_file)
{
cout<<"can'topenfile!"<<endl;
return1;
}
output_file<<str<<endl;
output_file.close();
output_file.open("CodeFile.txt");
if(!output_file){
cout<<"can'toenfile!"<<endl;
return1;
}
for(i=0;i<strlen(str);i++){
for(j=0;j<=n;++j)
{
if(HT[j].ch==str[i])
{
output_file<<HC[j];
break;
}
}
}
output_file.close();
cout<<"n";
cout<<"编码完毕,并且已经存入CodeFile.txt文件!n";
input_file.open("CodeFile.txt");//从CodeFile.txt中读入编码,输出在终端
if(!input_file)
{
cout<<"can'toenfile!"<<endl;
return1;
}
input_file>>code;
cout<<"编码码值为:"<<code<<endl;
input_file.close();
}
elseif(choice=='D'||choice=='d')//读入CodeFile.txt中的编码进行译码,将译出来的字符放入Textfile.txt中
{
input_file.open("CodeFile.txt");
if(!input_file){
cout<<"can'toenfile!"<<endl;
return1;
}
input_file>>h;
input_file.close();
output_file.open("Textfile.txt");
if(!output_file)
{
cout<<"can'toenfile!"<<endl;
return1;
}
k=0;
while(h[k]!='�')//先用编码中的前几个和字符的编码相比较,然后往后移
{
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
l=k;
for(j=0;j<strlen(HC[i]);j++,l++){
hl[j]=h[l];
}
hl[j]='�';
if(strcmp(HC[i],hl)==0)
{
output_file<<HT[i].ch;
k=k+strlen(HC[i]);
break;
}
}
}
output_file.close();
input_file.open("Textfile.txt");
if(!input_file){
cout<<"can'toenfile!"<<endl;
return1;
}
input_file>>h;
cout<<h<<endl;
input_file.close();
cout<<"译码结束,字符已经存入Textfile.txt文件中!"<<endl;
}
elseif(choice=='Q'||choice=='q')//退出程序
{
exit(0);
}
else//如果选了选项之外的就让用户重新选择
{
cout<<"您没有输入正确的步骤,请重新输入!"<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
return0;
}
六、测试情况
编码译码
数据存储情况
 爱华网
爱华网