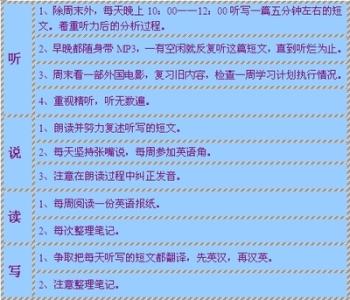
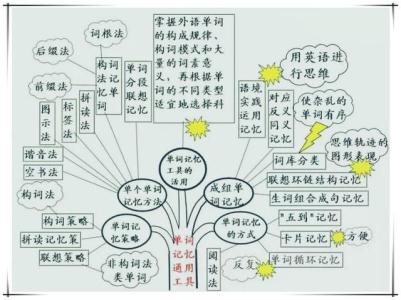
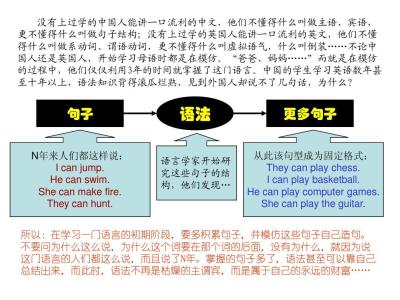
动词的过去、现在和未来动词时态一览表 下面,我们来看看各个时态的用法:
一般过去时
用法索引
1.在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。
时间状语有:yesterday,last week,an hour ago,the other day,in 1982等。
Where did you go just now?
2.表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。
When I was a child,I often played football in the street.
特殊句型(需重点掌握)
1.It is time for sb.to do sth.“到……时间了”、“该……了”
2.It is time sb.did sth.“时间已迟了”、“早该……了”
It is time for you to go to bed.你该睡觉了。
It is time you went to bed.早该睡觉了。
3.would (had) rather sb.did sth.表示“宁愿某人做某事”
I’d rather you came tomorrow.
请你注意:一般过去时的时间状语应该是表示过去某个时间的词或词组,如:yesterday,last month,in 1999,two days ago等,绝对不可与recently,in the past 10 years,this month等连用,因为这样的时间状语都与现在有关系,应该用现在完成时或一般现在时。
过去进行时
用法索引
1.表示过去某个时刻或某一阶段正在进行的动作。 构成: be(was,were)+现在分词,常用的时间状语:at 10:30 last night ,this time yesterday evening
Eg1.What were you doing at three o’clock yesterday afternoon?
2.用于when,while 引导的时间状语从句中。用过去进行时表示较长的动作。过去进行时可用于主句,也可用于从句。
Eg1.I was doing my homework when someone knocked at the door.
Eg2.We were walking along the river when suddenly it rained.
Eg3.While he was waiting at the bus stop,the traffic accident happened.( While 后的分句必须用进行时)
Eg4.While I was reading ,my sister was sleeping.(表示对比,都用进行时)
3.用于表示过去将来的动作。常用在间接引语中。
Eg1.She was leaving early the next morning.
Eg2.I asked him whether he was coming back for dinner.
过去将来时
用法索引
1.过去将来时表示从过去的某一时间来看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。它常用于宾语从句中。
有两种构成形式:用would表示的过去将来时和用be (was/were) going to 表示的过去将来时。
Eg1.He told me he would go to Beijing.
Eg2.He said the train was leaving at six the next morning
Eg3.She said she was going to start at once.
过去完成时
用法索引
1表示过去某时开始,一直持续到另一时间和状态。即动作完成于某个过去时间之前。常用的时间状语:由by,before等词构成的表示时间的介词短语。“过去的过去”这种逻辑关系常通过上下文体现出来,而不一定受某个时间状语的限制。
We had not heard from him by the end of last year.
2.根据时态一致的原则,在从句中谓语动词要用过去完成时代替其他时态。
She said she had learned French for six years.构成
一般现在时
用法索引
1.经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用。
时间状语: every…,sometimes, at…,on Sunday
I leave home for school at 7 every morning.
2.客观真理、客观存在、科学事实。
The earth moves around the sun.
Shanghai lies in the east of China.
3.表示格言或警句中。
Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。
请你注意:
此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例:Columbus proved that the earth is round.
4.现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。
I don’t want so much.
Ann Wang writes good English but does not speak well.
现在进行时
用法索引
1.表示说话时正在进行的动作。常和now,Look!Listen!或其他铺垫句及情景设置句连用。
Eg1.I am reading a book now.
Eg2.Look!They are having a basketball match.
Eg3.Listen!He is playing the piano.
Eg4.It’s 7:00 pm.The Greens are watching TV.
2.表示现阶段正在进行着的动作但说话时不一定正在进行。
Eg1.He is working in a shoe factory these days.(临时性的工作)
Eg2.Mr.Green is writing another novel. (说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)
3.表示在近期按计划或安排要进行的动作。即用现在进行体表示将来要发生的动作。但一般要与将来时间连用,而且仅限于少量动词。例如: come,go,start,arrive,leave,stay等。
Eg1.Mr.Smith is leaving for London tomorrow.
Eg2 Are you staying here till next week?
4.常与表示渐变的动词连用。例如: get,grow,become,turn,,begin等。
Eg1.The leaves are turning red.
Eg2.It’s getting warmer and warmer.
现在完成时
用法索引
1.表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。常用的时间状语:already,get,never,just,before,recently,for+一段时间,since+一段时间
I have lost my key.(说明过去某时丢的,现在还未找到。)
2.表示过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
I have known him for ten years.
The dog has been dead for three days.
3.表示从过去到现在之间曾经经历过的事。
We have been to the Summer Palace twice.
请你注意:
因为含有for加一段时间或since加一个时间点这样的时间状语的完成时,有动态和延续性的特点,所以不能使用终端动词或瞬间动词。
例:My sister has been here for 5 days.(过去分词做表语表示状态,可以延续)
My sister came here 5 days ago.(终端动词)
现在完成进行时
用法:表示某一动作开始于过去某一时间,延续或重复地出现至今,或将继续延续至将来。
例:We have been working on this project for over a month now.(到目前为止,我们一直在处理那个项目,已经花了一个多月时间了。)
请你注意:现在完成进行时与现在完成时相比,现在完成进行时更强调:在从过去到现在的时间里,动作或状态一直持续或一直反复出现。
一般将来时
用法索引
1.一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。

2.表示将来经常或反复发生的动作,常与表示将来的时间状语连用。
如:tomorrow,tomorrow morning,next week(year,term…),in (two days…),soon,the day after tomorrow等。
3.问对方是否愿意或表示客气的邀请。
4.shall用于第一人称,常被will 所代替。will 在陈述句中用于各人称,在征求意见时常用于第二人称。
 爱华网
爱华网