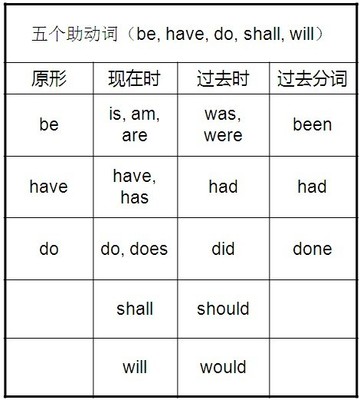
情态动词的推测性用法的几种结构:
A. 情态动词+BE+ 表语。表示对现在情况的推测。
It can’t be true. He must be a professor.
They should be back by now.
B. 情态动词+动词进行体。表示对现在正在进行的情况进行推测。
You shouldn’t be working like that.
Let’s hurry up. They must be waiting for us
He can’t be telling the truth.
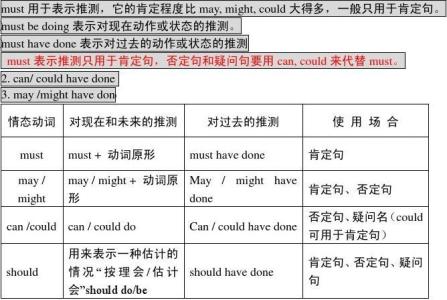
C. “情态动词+have+过去分词”表示对过去某种行为的推测。情态动词的这种用法是各类考试中测试的重点内容,应该充分注意。
①must have+过去分词,意思是“想必,一定已经……”表示对过去已发生的事情进行肯定推测判断。
---“Why isn’t he here?”
---“He must have missed the bus”
It must have rained last night. The ground is wet.
I think my letter must have been miscarried.
②can not/can’t/couldn’t +have+过去分词,意思是“某件事情(过去)不可能发生,表示对过去发生的事情可能性进行否定推测判断。
Li Ping can’t have been home. I saw her just now.
You can’t have finished your homework in such a short time.
She can’t/couldn’t have seen the film last year, it was on only recently.
③can/could+have+过去分词,表示对过去已发生的事情进行推测判断,常用于疑问句中。
Can /Could she have lost the book borrowed from the library?
注:could have +过去分词偶尔也可以用在否定句中,表示过去某事本可以发生,但是却没有发生。
It was too dark last night. You could have lost your way.(事实上并没有迷路)。
④May/Might +have+过去分词,表示对过去已发生的事进行推测判断,一般只用于肯定句或否定句中,不用于疑问句中。May/Might +have+过去分词的意思是“可能已经”,“或许”;may/might not+have+过去分词的意思是“可能不(没有)”。
You might have read the book before. The train may have left already.
You were so careless that day. You might have make a bad mistake.(事实上并没有犯错误)。
She might not have noticed the warning on the wall. That was why he parked there.
⑤should/ought to+have+过去分词:表示过去本应该做而实际上并未做的事,并含有责备的意思。
eg, You should/ought to have come five minutes earlier.你应该早来五分钟的(而实际上并没有)。
注:它的否定式shouldn’t /oughtn’t to +have+过去分词 则表示做了不该做的事。
eg, You shouldn’t/oughtn’t to have kept the books in the damp place.(而实际上书已放在潮湿的地方了)
⑥needn’t +have+过去分词:表示本来不必做某事而实际上已经做了某事,强调“不必要……”常有责备之意。
eg, You needn’t have woken me up; I don’t have to go to work today.(而实际上已把他叫醒了)。
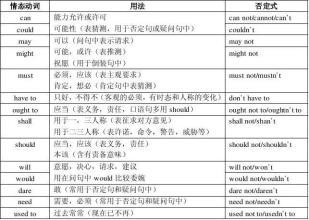
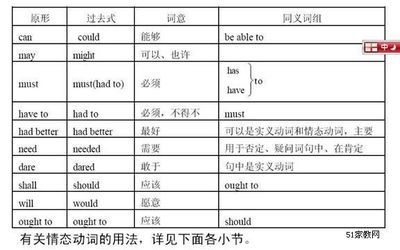
在上述结构中,can / could主要用于否定句和疑问句; may / might主要用于肯定句,间或用于否定句,但不用于疑问句;must只用于肯定句;should / ought to 可用于肯定句和否定句,但不用于疑问句;need只用于否定句。
几道习题:
1. John Glenn’s return to space at the age of 77 demonstrates that aging , but enjoyed.
A needs not be feared B. need not be feared
C. doesn’t need be feared D. be not feared
2. Richard went to the shop because he a suit for his job interview.
A. need to buy B. needed to buy
C. needed buy D. did need buy
3. He gave up politics when he a great career in it.
A. must have made B. might make
C. might have made D. need have made
4. A traveler who once set his foot on that land the great changes happening there.
A. must have noticed B. must notice
C. must be noticing D. would have noticed
5. -----I’ve been looking for you all day.
-----you couldn’t all day.
A. have swum B. be swimming
C. have been swimming D. to swim
6. The formal opening ceremony of the exhibition hours ago.
A. ought to be begun B. ought to begin
C. ought to have been begun D. ought to have begun
7. You such a long essay. The teacher only asked us to write 300 words, and you have written 600.
A. mustn’t have written B. needn’t have written
C. didn’t have to write D. didn’t need to write
8. -----I saw Jane at the party last night.
-----You her because she had gone abroad with her parents.
A. couldn’t have seen B. couldn’t see
C. mustn’t have seen D. needn’t have seen
9. -----it’s time for supper. Jacob is still in his room.
-----He about the question his teacher raised.
A. might still be thinking B. might still think
C. might still have thought D. still thinks
10. -----Bob earns more in one day than I do in a week.
----- He very wealthy.
A. must have been B. has to be
C. must be D. has to have been
11. What are you doing now? You your textbook instead of wasting time on the novel.
A. should have been reading B. should read
C. would have read D. should be reading
12. -----What can I do for you?
-----If you see Mr. Allen, give him my regards.
A. should B. would C. shall D. will
13. Since the flight has been cancelled because of bad weather, we by train.
A. Ought to have gone B. might as well go
C. had better to go D. would rather not
14. It’s claimed that as many as 2 billion people the opening game of the 1998 would cup held in France.
A. should watch B. might watch
C. might watch D. may have watched
15. These cells cannot be used any more. You them in some dry place.
A. need to put B. could put
C. should have put D. must have put
 爱华网
爱华网