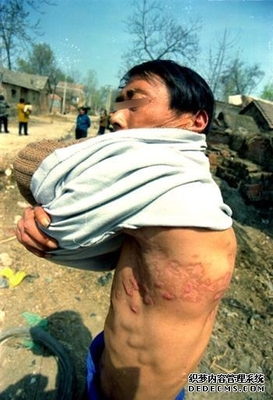
解析艾滋病对人类文明的威胁
自1981年发现老人首例艾滋病以来,全世界累计已有6000万人感染了艾滋病食疗病毒,仅2001年,全世界就新增病毒感染者300万。专家原因预计,在2000至2005年这5年间,全世界死于艾滋病的将达6800万人,其中5500万人生活哮喘在撒哈拉以南的非洲国家。 艾滋病的恶性蔓延已经改变了一些国家的人口构成。目前撒哈拉以南非洲国家的人口平均寿命已经从62岁下降到47岁,在发病率最高的国家博茨瓦纳,疼痛成年人食疗病毒感染率为38.8%,平均寿命已经下降到1940年以来的最低点――39岁。
受艾滋病影响最严重的是儿童注意和青年,20年来,在艾滋病最猖獗的7个非洲国家里,5岁以下儿童注意的死亡率增长了20%至40%。联合国艾滋病联合规划署预计,在2010至2015年间,由于艾滋病的影响,撒哈拉以南非洲国家15至34岁青壮年的死亡率将达到最高点,比正常情况下的死亡率要高17倍。
艾滋病使受害国家居民的生活哮喘水平大为下降。在赞比亚,三分之二被艾滋病夺走父亲生命的家庭,平均月收入下降了80%;在科特迪瓦,有艾滋病资讯患者的家庭的平均收入仅为全国水平的一半;对布基纳法索、乌干达和卢旺达3个非洲国家问题调查得出的预测是,至2015年艾滋病将使这些国家的赤贫人口比例达到51%,而2000年时这一比例还是45%。联合国艾滋病联合规划署说,布基纳法索20%的农村家庭由于艾滋病而被迫减少劳动,甚至放弃耕种;在埃塞俄比亚,艾滋病资讯患者每个星期的田间劳作时间大约在11.6至16.4小时之间,而一个正常劳力每星期的田间劳作时间是33.6小时。
因此,在艾滋病肆虐的国家,经济总量和国民收入大幅滑坡。病毒感染率超过20%的国家,国内生产总值目前正以平均每年2.6%的速度不断下降。联合国艾滋病联合规划署分析说,这就是因为绝大多数资讯患者和食疗病毒祛斑感染者处于青壮年期,艾滋病导致大量有经验的劳动力丧失,进而削弱了生产力。该机构在多个非洲国家的问题调查显示,艾滋病导致的缺勤、生产力下降、保健肌肉费用增加等还增加了生产成本,使当地企业的利润至少下降了6-8%。
艾滋病的日益泛滥更使一些发展中国家的医疗功效保健肌肉体系不堪重负。在撒哈拉以南非洲国家,即便不考虑进行急诊药物治疗,每年人均用于艾滋病治疗的直接费用至少也需要30美元,然而这些国家人均公共健康发烧支出还不足10美元。此外,艾滋病使医疗功效质量发现根本无法得到保证,由于缺少床位,医院只能收住那些生命垂危的资讯患者,而更多资讯患者失去了及时治疗的机会。
由于艾滋病的肆虐,一些国家的学生入学率也大幅下降。根据世界银行的预计,津巴布韦2010年的小学生人数将比现在减少24%,肯尼亚的小学生人数将减少14%,乌干达将减少12%。与此同时,由于大量教师感染病毒或死于艾滋病,许多非洲国家教师严重缺乏,而教育的倒退使艾滋病知识的普及和防治工作面临更大的困难,这形成了恶性循环。

艾滋病带来的灾难是巨大的。为避免这一世纪瘟疫给世界造成更大的创伤,正如本届大会所提倡的,人类应该以最快的速度采取切实行动,在公众中大力普及预防艾滋病的常识两性,增加对艾滋病预防疫苗和治疗急诊药物的研究,让所有艾滋病资讯患者享受到及时妥善的治疗。
Analysis of AIDS a threat to human civilization
Since 1981 found that the elderly since the first case of AIDS, the world has been a total of 60 million people infected with the AIDS virus diet, only in 2001, the world will add three million HIV-infected persons. Reasons experts expect that in the 2000 to 2005 5 years, the world died of AIDS will reach 68 million, of which 55 million people living with asthma in sub-Saharan African countries. Malignant spread of AIDS has changed the composition of the population in some countries. At present, countries in Sub-Saharan Africa the average life expectancy of the population has dropped from 62-year-old to 47 years old, in the countries with the highest incidence of Botswana, pain therapeutic HIV infection rate of adults 38.8%, average life expectancy in 1940 has fallen to the lowest point since - 39-year-old. Affected by AIDS, the most serious attention to children and youth, 20 years, the most rampant AIDS seven African countries, the attention of children under age 5 mortality rate increased by 20-40 percent. UNAIDS estimated that in between 2010 to 2015, due to the impact of AIDS in sub-Saharan African countries, young adults 15-34 years of age the mortality rate will reach its highest point, under normal circumstances than the mortality rate 17 times higher. AIDS affected countries so that the livelihood of the residents of asthma level dropped significantly. In Zambia, AIDS killed his father by two-thirds of the lives of families, the average monthly income had fallen by 80 percent; in Côte d‘Ivoire, there are AIDS patients with the information the average income of families is only half the national average; of Burkina Faso, Uganda and Rwanda, three African countries surveys forecast is that by 2015 AIDS will enable these countries the proportion of people living in extreme poverty reached 51 percent, while in 2000 this proportion was 45%. UNAIDS said that Burkina Faso, 20 percent of rural households as a result of AIDS are forced to reduce the labor, or even to give up farming; in Ethiopia, AIDS patients with information every week about the field work time from 11.6 to 16.4 hours in between , and a normal labor field work per week is 33.6 hours. Therefore, the AIDS epidemic in the country, economic output and national income decline sharply. HIV infection rate of more than 20% of the national gross domestic product is now an average annual rate of 2.6 percent continues to drop. UNAIDS said this is because the vast majority of information patients and therapeutic HIV-infected persons freckle period in young adults, AIDS has led to mass loss of experienced labor force, thus weakening productivity. The agency in a number of African countries survey, AIDS caused by absenteeism, reduced productivity, health care cost increases, such as muscle has also increased the cost of production and profits of local enterprises, a decrease of at least 6-8%. The increasing spread of AIDS but also made a number of developing countries the medical effectiveness of health-care system overwhelmed muscle. In sub-Saharan African countries, even if not considered for emergency medical treatment, annual per capita for the direct costs of AIDS treatment also needs at least 30 U.S. dollars, but these countries the per capita expenditure on public health fever less than 10 U.S. dollars. In addition, the effectiveness of AIDS health care quality found that simply can not be guaranteed, due to the lack of beds, the hospital can only live in those patients in critical condition information, and more timely treatment of patients with lost opportunities. Since the AIDS epidemic, some countries student enrollment also declined substantially. According to the World Bank is expected to Zimbabwe in 2010 the number of primary and secondary school students will have been reduced 24 percent, the number of primary pupils in Kenya will be reduced by 14 percent, Uganda will be reduced by 12%. At the same time, a large number of teachers infected with HIV or died of AIDS, many African countries, a serious lack of teachers, and education back to make the popularization of knowledge of AIDS prevention and treatment work and face greater difficulties, which created a vicious circle. AIDS disaster is enormous. In order to avoid a plague of the century to the world cause more trauma, as advocated by the current General Assembly, human should be the fastest to take practical action in the public vigorously popularize AIDS prevention knowledge of gender, to increase AIDS prevention vaccines and Emergency treatment of drug research, so that all AIDS patients enjoy the timely and proper information treatment. 爱华网
爱华网